Tutorial #05 : point cloud cleaning
Point cloud cleaning
Welcome to the 3DF Zephyr tutorial series. This guide will present the tools for cleaning point clouds.
The tutorial targets all 3DF Zephyr Versions.
Summary
Introduction
Manual editing is often used to remove noise in the generated point clouds. Although the confidence removal tool can clean the most noise out of the point cloud automatically, sometimes some manual editing is required for even better results.
The point cloud cleaning tools
Load any dataset you wish to experiment with and ensure you have generated at least the Sparse point cloud.
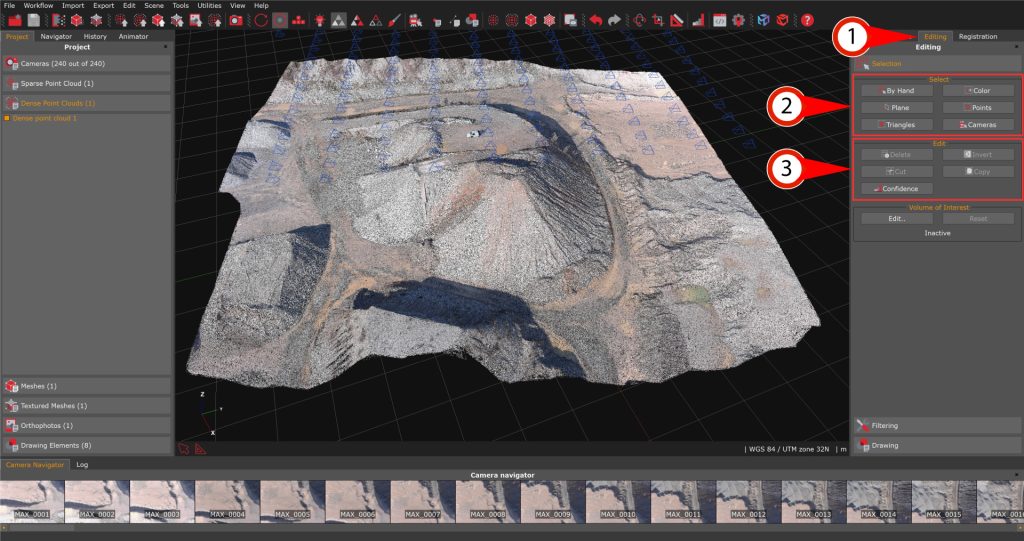
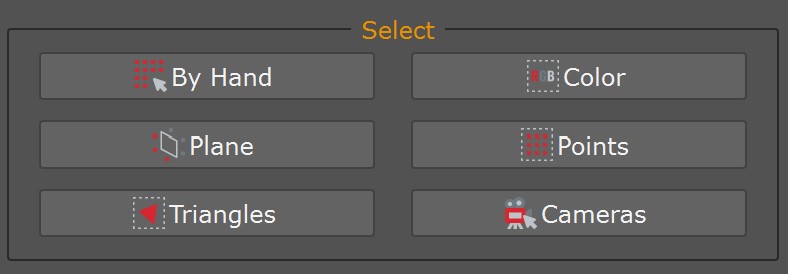
Select the “Editing tab (1)” to access the editing tools. In there, you can notice two different sections: the “Select” (2) section; and the “Edit” (3) section.
The “Select” section offers you tools useful for selecting points in many ways and then, when selected, editing them with a tool in the “Edit” (3) section.
The manual selection tools
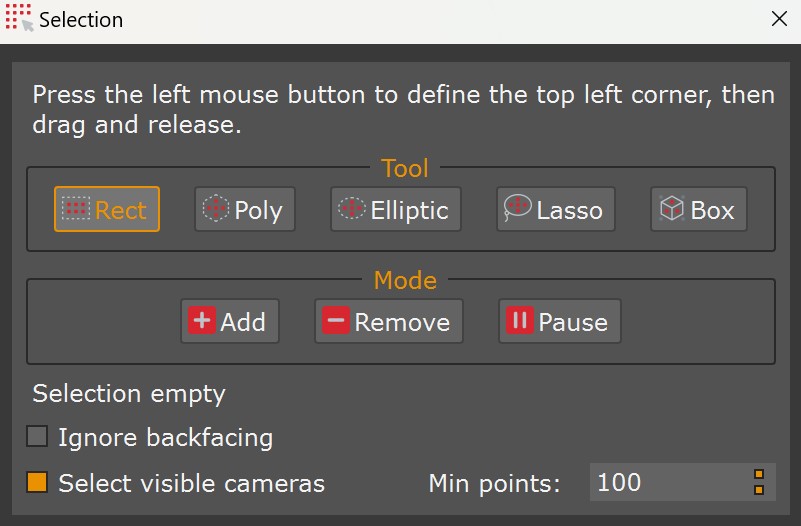
Clicking on the “By hand” selection mode icon to open the manual “Selection” window, where you can find different manual selection tools:
– Rect icon: drags a rectangle on the workspace, and all the inside points will be selected (highlighted in red).
– Poly icon: click the points of a polygon (and close the polygon so that the last point as the same initial point). Similarly, all the selected points will be highlighted in red.
– Elliptic icon: draws a circle on the workspace.
– Lasso icon: allows for a free-hand selection.
– Box icon: select points inside a box.
Additionally, the Mode section offers three usage modes for helping the selection:
– Add mode can be used to add currently selected points to the selection.
– Remove mode can remove currently selected points from the selection.
– Pause/Resume mode can be used to pause – resume the selection mode and switch it to the overview mode.
The Edit section below allows to Delete, Copy, Invert, and Cut the selected points.
The other selection tools
The following selection tools offer other methods to select points:
- – Color: select the 3D object you want to focus on (dense cloud or mesh), pick the point/polygon color that you want to select (either by using the color selector or choosing it on the scene), and all the color values falling behind a certain (customizable) threshold will be selected (and highlighted in red). As usual, you can remove these points using the “Delete” button in the Editing tab’s Edit section.
– Plane: move the plane where needed, and all the points above the plane surface will be selected (highlighted in red).
– Triangles: this tool works on the mesh (automatically selected) and allows you to select triangles using different filters.
– Points: this tool works only on sparse and dense point clouds and allows you to select points using different filters.
– Cameras: This tool allows you to select the cameras in the workspace.
Some users may also want to use the “Confidence” tool to remove the points in which Zephyr has less confidence, which usually happens to be noise.
After the selection, you can also use the “Cut” and “Copy” tools (which do not work on the sparse point cloud) to split or make a copy of selected points. Or you can “Invert” the selection. The same Manual tools can be used to remove parts of meshes.
The next tutorial will show how to record a movie directly inside Zephyr. Proceed to the next tutorial.